Abstract

Introduction: MAS is a severe, life-threatening complication of rheumatic diseases such as Still's disease and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). MAS is a form of secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, characterized by a hyperinflammatory state caused by immune cell dysregulation which can lead to multiorgan damage. Sustained activation and expansion of T lymphocytes and macrophages stimulates the hypersecretion of proinflammatory cytokines such as IFNγ.
The mainstay of treatment for MAS is high doses of glucocorticoids (GCs); however, they do not always provide adequate control in all patients. Additional treatments are used without a standardized approach; however, morbidity and mortality remain high. Preliminary data from a pilot study including 9 patients with inadequate response to high-dose intravenous GCs (NCT03311854) showed that emapalumab, a fully human anti-IFNγ monoclonal antibody, led to rapid neutralization of IFNγ and was efficacious in controlling MAS with a favorable safety profile [De Benedetti et al. Annals Rheumatic Dis 2020;79(Suppl. 1):194]. A study to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of emapalumab in patients with MAS in Still's disease and SLE is enrolling patients.
Objective: To describe the design and objectives of a Phase 2/3 study aiming to confirm the efficacy and safety of emapalumab in the treatment of MAS in rheumatic disease.
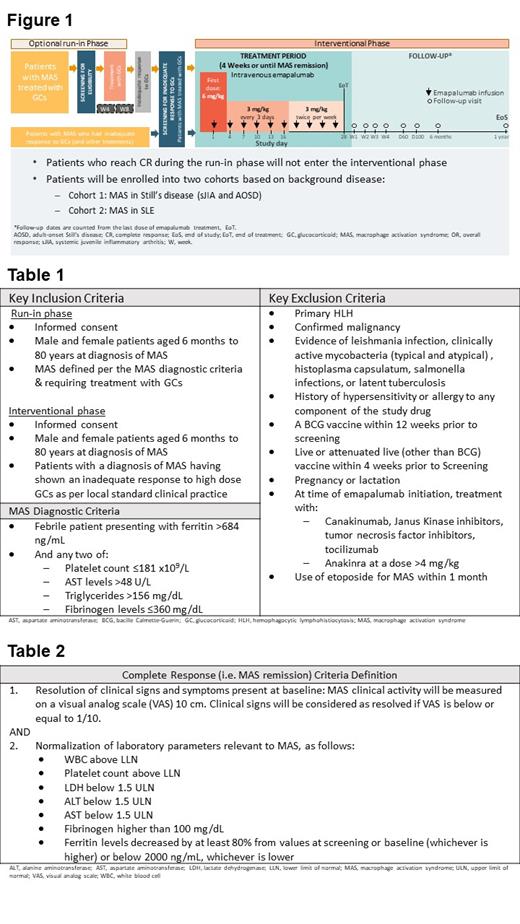
Study Design and Methods: This open-label, single arm, multicenter, interventional study (Figure 1) is enrolling pediatric and adult subjects into two cohorts 1) MAS in Still's disease (systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and adult onset Still's disease; n=25) and 2) MAS in SLE (n=16). Eligible patients must present with an inadequate response to high doses of GCs. Each cohort is a single-arm study composed of two phases: an optional run-in phase and an interventional phase. Key eligibility criteria vary by cohort and phase (Table 1). During the run-in phase, patients are treated with GCs according to the investigators' clinical practice and followed until MAS remission or inadequate response, or for a maximum of 12 weeks. Patients with an inadequate response to GCs (and potentially to other therapies) enroll in the interventional phase to be treated with intravenous emapalumab (initial dose 6mg/kg, subsequent doses 3mg/kg) for 4 weeks or until a complete response (CR) is achieved, and are followed off-drug for 1 year.
Based on the assumptions of a successful treatment with GCs (null hypothesis) of up to 40% for cohort 1 (i.e. CR rate of 40%) and 30% for cohort 2 (i.e. CR rate of 30%), if the truth is 70% complete responders (for both cohorts), then a total of 25 and 16 patients, respectively, is required to demonstrate a statistically significant proportion of CR with a power of 80% using a one-sided exact binomial test at a significance level of 2.5%. The study design for cohort 1 is a group sequential design, including an interim analysis assessing efficacy with an adjusted type 1 error after 16 patients have reached Week 8 after the first dose of emapalumab.
The primary endpoint of the study is CR (response criteria defined in Table 2) at Week 8 after first emapalumab administration. Secondary efficacy endpoints include GC tapering, survival, time to first CR, overall response (CR and partial response), time to first overall response, MAS recurrence, PK/PD profile of emapalumab, and patient-reported outcomes. Safety endpoints include assessments of adverse events, abnormal laboratory parameters, and anti-drug antibodies.
Summary: This ongoing trial is designed to address the unmet need for new efficacious and safe therapies for the treatment of MAS.
Grom: AB2 Bio: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy. Bachir: Sobi: Current Employment. Asnaghi: Sobi: Current Employment. De Benedetti: Novimmune: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sobi: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Emapalumab-lzsg is an IFN-gamma blocking antibody indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric (newborn and older) patients with primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) with refractory, recurrent, or progressive disease or intolerance with conventional HLH therapy.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal